EDITORIAL
The results of recent studies show that tumor biology, coagulation activation, and inflammatory reactions profoundly contribute to the thrombosis pathogenesis in cancer as well as tumor progression, metastasis, and developing chemoresistance. Cancer is an independent predictor of thrombosis. During carcinogenesis, tumor cells express proinflammatory cytokines, proangiogenic and procoagulant factors, and also stimulate other cells to express various components promoting emerging thromboinflammation. The discovery of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) provides an opportunity to take a new look at biology and a role neutrophils may play in thromboinflammation and tumorigenesis. The close interplay between tumor cells, tumor-associated neutrophils and NETs as well as other players in the tumor microenvironment underlies activation of thromboinflammation in cancer patients not only resulting in thrombus formation, but also promoting tumor growth and dissemination.
ОRIGINAL ARTICLES
What is already known about this subject?
► External genital endometriosis (EGE) is an immune-inflammatory estrogen-dependent pathological process.
► It is evidenced about a relation between intestinal dysbiosis and impaired estrogen metabolism, an imbalance in innate and adaptive immune arms, as well as formation of chronic inflammation in specific pathologies.
► Previous studies provide convincing evidence about changes in intestinal biocenosis during developing NGE.
What are the new findings?
► It has been shown that patients with EGE, compared to healthy women, are characterized by lower bacterial α-diversity.
► The pattern of the taxonomic composition for intestinal microbiota in patients with EGE at the level of phylum and genera was clarified.
► Significant correlations between specific bacterial genera and systemic levels of estrogen and proinflammatory cytokines have been identified.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The role for intestinal dysbiosis as a crucial factor in EGE pathogenesis has been proven.
► Targeting the intestinal microbiota may help improve effectiveness of therapeutic approaches in EGE treatment.
Aim: systemically assessed characteristics of intestinal microbiota taxonomic composition in relation to parameters of hormonal and immune status in patients with external genital endometriosis (EGE).
Materials and Methods. The controlled cross-sectional study included 33 patients with EGE comprising main group, and 30 healthy women enrolled to control group. All women underwent assessment of hormonal status and cytokine expression levels in peripheral blood. Level of blood hormones estradiol (E2), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), prolactin (PRL) was carried out using enzyme-linked immunosorbent and chemiluminescent assays. Expression levels of cytokines such as interleukin (IL) IL-6, IL-8, tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) were analyzed by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Taxonomic composition of intestinal microbiota at the level of phyla and genera was carried out by 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequencing. Microbial community a-diversity, the Chao1, ACE, and Sobs indices were used.
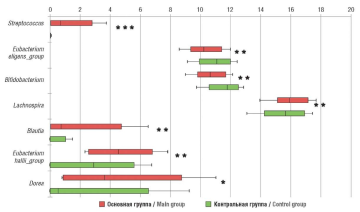
Results. The concentration of blood E2 in main group was significantly higher compared to control group. Also, women with EGE had higher plasma concentrations for IL-6, IL-8, IL-17 and TNF-a compared to those in control group (p < 0.001). While analyzing bacterial community a-diversity in main group, Chao1 index was found to be significantly decreased. At the phylum level, the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio was increased in patients with EGE compared with that in control group. Among the 20 largest genera in patients with EGE, significant abundance was observed for Lachnospira, Blautia, Dorea, Streptococcus, Eubacterium hallii_group paralleled with significant decline in Bifidobacterium and Eubacterium eligens_group. A positive correlation was obtained between estrogen levels and the number of representatives from the genera Eubacterium hallii_group and Streptococcus, IL-8 and Streptococcus, TNF-α and Streptococcus and Lachnospira, as well as a negative correlation between TNF-α and Bifidobacterium.
Conclusion. A relation between dysbiotic intestinal alterations and developing endometriosis was found. The identified correlations between altered taxonomic composition of the intestinal microflora and parameters of hormonal and immune status in patients with EGE suggest that intestinal microbiota is involved in pathophysiology of endometriosis.
What is already known about this subject?
► Antiphospholipid antibody (APA) carriage strongly affects developing complicated pregnancy. The incidence of habitual miscarriage, according to various sources, ranges from 7 to 42 %. Also, the presence of high APA titers plays an important role in the pathogenesis of thromboembolic complications, which have a high mortality rate.
► There is a need to develop a prevention and prognosis system that could prevent development of placenta-associated complications representing a very urgent task. Unfortunately, at present, despite the use of various preventive and therapeutic methods, it was impossible to reduce the incidence of preeclampsia and fetal growth retardation.
What are the new findings?
► Intravenous immunoglobulins (IVIG) use in combination with acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) and low molecular weight heparins (LMWHs) achieved a high frequency of favorable pregnancy outcomes.
► While analyzing the data of histologically examined placentas, there were found significant differences. The incidence of placental insufficiency was significantly lower in IVIG group, and in most cases the normoplastic type of placenta structure was confirmed histologically.
► Comparing the relative expression area for annexin V, CD 34+, KiSS-peptine and its KiSS1R receptor revealed significant differences: for anticoagulant protein annexin V it was 2.3-fold higher in patients who received IVIG during pregnancy; endothelial marker CD34+ – 4-fold higher, KiSS-peptine – 2.3-fold higher, and its KiSS1R receptors– 5.4-foldhigher in the placenta from women who received IVIG therapy starting from early pregnancy stage.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Placenta immunohistochemistry examination by method assessing the relative expression area for anticoagulant protein annexin V, endothelial marker CD 34+, KiSS-peptine and its KiSS1R receptors can be used as a highly effective method of controlling the effectiveness of IVIG therapy.
► IVIG use in combination with LDA and LMWH will improve pregnancy outcomes in patients with history of AFA carriage and reproductive losses.
Introduction. The role of antiphospholipid antibody (APA) carriage in the pathogenesis of pregnancy failure is one of the most recently debated issues. To date, no unified therapeutic approach to immunotherapy of antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) in pregnancy exists. Intravenous immunoglobulins (IVIG) have become the drugs of choice to treat this pathology in pregnant women.
Aim: to evaluate an effectiveness of preventing placenta-associated complications (PACs) in patients with recurrent miscarriage and circulating APAs.
Materials and Methods. A prospective study was conducted to analyze the course of pregnancy and outcomes in 150 patients who had diagnostic APA titers and aggravated obstetric and gynecological anamnesis. All pregnant women received therapy with low-dose aspirin (LDA) and low molecular weight heparin (LMWHs). In addition to combining LMWHs and LDA, 126 (84.0 %) pregnant women received IVIG courses administered at gestational age of 6-8, 12-14, and 22-24 weeks.
Results. Based on the data obtained, gestational complications such as chronic placental insufficiency, hemodynamic disorders, fetal growth retardation, gestational arterial hypertension, moderate preeclampsia (PE) were significantly more frequent in patients receiving no IVIG during pregnancy. It should be noted that development of severe obstetric complications, such as severe PE, premature detachment of a normally located placenta, massive blood loss, and antenatal fetal death were not observed in any case. No patient developed venous thromboembolism during pregnancy and in the postpartum period. Comparing relative expression area of annexin V, CD 34+, KiSS-peptine and its receptors (KiSS1R), there were revealed significant differences. The relative expression area for anticoagulant protein annexin V was 2.3-fold higher in IVIG-treated patients in pregnancy; endothelial marker CD34+ - 4-fold higher, KiSS-peptine - 2.3-fold higher, and KiSS1R - 5.4-fold higher in placenta from women treated with IVIG starting from early pregnancy stage.
Conclusion. In order to assess the effectiveness of PAC prevention in patients with habitual miscarriage and circulating APAs, it is possible to estimate relative expression area for placental anticoagulant protein annexin V, endothelial marker CD 34+, KiSS-peptine and KiSS1R.
What is already known about this subject?
► Currently, the implementation of distinct scenarios for intrauterine, intraamniotic maternal and fetal infection poses one of pressing issues in obstetrics and perinatology.
► Chorioamnionitis (CA) is a common cause of premature birth able to result in adverse fetal consequences, including those affecting central nervous system with regard to a risk of developing cerebral palsy.
► Even in the presence of risk factors, premature rupture of water in full-term and premature pregnancies, not all women develop CA and associated maternal and fetal complications. Нence, it accounts for a need to search for additional predisposing or background maternal conditions, which markedly increase a risk of severe CA complications.
What are the new findings?
► In addition to risk factors directly related to the infectious and inflammatory unfavorable background (acute respiratory viral infections, influenza, COVID-19 suffered during pregnancy, acute gestational pyelonephritis, asymptomatic bacteriuria, vaginitis and/or cervicitis, the presence of group B streptococcus), a great percentage of obstetric complications (preeclampsia, placental insufficiency, premature birth) is also observed.
► Combinations of high-risk gene alleles underlying severe neonatal infection in maternal CA have been identified.
► The established combinations of genotypes forthe genes Fc-gamma receptor IIa, interferon gamma, interleukin 6, mannose binding lectin 2 represent crucial additional risk factors for development of severe intrauterine infection in patients with CA.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The study data evidence about the importance of identifying genes for developing CA and septic neonatal complications to optimize and personalize management of high-risk patients (premature birth, infections during pregnancy, premature rupture of membranes).
► The data obtained may be further used in obstetrics and perinatology.
Aim: to determine clinical, anamnestic and molecular-genetic parallels in emergence of clinical chorioamnionitis (CA) and severe forms of intrauterine infections (IUI) in high-risk pregnant women.
Materials and Methods. A single-center prospective cohort comparative case-control study was conducted by examining 58 pregnant female patients aged 18 to 42 years with a verified CA diagnosis during pregnancy and childbirth at different gestation stages (main group), and 35 age-matched pregnant women with uncomplicated pregnancy and no significant extragenital pathology, aggravated factors of obstetric and gynecological history and risk factors for developing CA (control group), observed and performed a delivery in Yudin City Clinical Hospital. All women underwent clinical, anamnestic, laboratory, instrumental and molecular-genetic examitation. We studied the polymorphism of genes FCGR2A (Fc fragment of immunoglobulin G receptor IIa), IFN-γ (interferon gamma), IL-10 (interleukin-10), IL-6 (interleukin-6) and MBL2 (mannose binding lectin 2) to determine their role in assessing a risk of maternal and neonatal infection.
Results. Among the patients with developed clinical CA vs. control subjects, more of them had a history of abortion and miscarriages (17.24 %), comorbid with chronic arterial hypertension (13.79 %), previous surgical interventions (27.59 %), as well as chronic inflammatory diseases (chronic tonsillitis, bronchitis, pyelonephritis, sinusitis; 27.59 % vs. 17.14 %). In addition to risk factors directly related to the infectious and inflammatory unfavorable background, they also had a significantly higher rate of obstetric complications: moderate preeclampsia - 6 (10.34 %) cases, threat of miscarriage or premature birth - 14 (24.14 %) cases vs. 1 (2.86 %) case in control group (p = 0.007), polyhydramnions - 4 (6.9 %) cases, placental insufficiency - 6 (10.34 %) cases. The frequency of premature rupture of membranes was 31.03 % in women with CA. Questionable cardiotocography (CTG) type was found in 24 (41.38 %) women with CA vs. 4 (11.4 3%) women without CA (p = 0.003), the pathological CTG type was observed only in women with CA. In the group with clinical CA and neonatal IUI, the combination of genotypes AG rs1801274 FCGR2A, TT rs2430561 (IFN-γ)+874, GC rs1800795 (IL-6)-174 occurs in 80.65 % (25/31), whereas in women without severe neonatal IUI - in 37.04 % (10/27) (odds ratio (OR) = 7.08; 95 % confidence interval (CI) = 2.166-23.166). In addition, the combination of alleles TT rs2430561 (IFN-γ)+874, GC+CC rs1800795 (IL-6)-174, AA rs1800450 MBL2 codon 54 was detected in 90.32 % (28/31) vs. 44.44 % (12/27) in main and control group (OR = 11.667; 95 % CI = 2.842-47.886), respectively.
Conclusion. The study data evidence about importance of identifying genes for developing CA and neonatal septic complications to optimize and personalize management of high-risk patients (premature birth, infections during pregnancy, premature rupture of membranes).
What is already known about this subject?
► The relevance of sepsis has been increasingly noticeable throughout the world, and obstetric sepsis has its own differences and often remains undiagnosed in a timely manner. The causative agents of bacterial obstetric sepsis are both Gram-positive and Gram-negative pathogens, as well as fungi and anaerobic bacteria; the most common pathogens are presented by group B streptococci, enterococci, Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae.
► In turn, Gram-negative sepsis is characterized by the formation of endotoxin, which becomes the main pathogenetic arm and accounts for severity of patient’s condition. Efferent extracorporeal techniques using various devices are used to remove endotoxin from the bloodstream. Each device uses different materials to adsorb endotoxin.
► Although endotoxin removal efficiency is critical to clinical effectiveness, there are few studies comparing the endotoxin removal efficiency between different devices.
What are the new findings?
► This article presents the results of using various sorption columns in an in vitro experiment with the introduction of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) corresponding to the pathophysiological threshold values of 12.5 μg and 37.5 μg for sepsis and severe septic shock, respectively.
► All studied cartridges can reduce endotoxin levels below the 12.5 μg level and even the 50 μg level. However, none of devices was able to lower LPS level from the “supercritical” 50 μg to the “critical” 12.5 μg.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Even a conventional poly(methyl methacrylate)-based dialyzer demonstrate an ability to sorb insignificantly some LPS amounts, that may be important while including such filters in renal replacement therapy in less severe conditions accompanied by inflammatory processes.
► When choosing a treatment method, the attending physician is limited both by procedure timing (2 hours or more) and by the number of devices used simultaneously or sequentially. In such limited conditions, the choice should be made in favor of a device that provides maximum efficiency, i.e., a cartridge capable of removing the maximum LPS amount, as demonstrated in the current research.
Aim: to assess the sorption capacity of various devices for endotoxin removal modelled in in vitro patient with septic shock experiment.
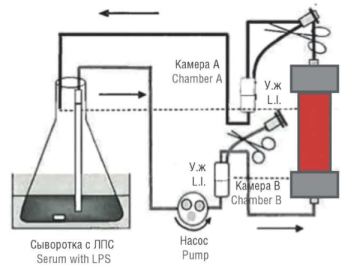
Materials and Methods. Endotoxin adsorption was evaluated in vitro by using circulating endotoxin solution in bovine serum in a closed circuit. The following columns were chosen for the experiment: Toraymyxin PMX-20R (РМ Х), Alteco® LPS Adsorber, Efferon LPS, Toray Filtryzer BK-2.1U. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) doses corresponding to severity of the septic process were sequentially added to a column pre-washed with physiological solution. The first LPS dose of 12.5 µg was added to a flask containing 1500 ml (1.5 L) of fetal bovine serum, a second LPS dose of 37.5 µg was added at 120 minute; the serum samples were collected before the onset of experiment, as well as 30, 60, 120 (before the second dose), 120 (after the second dose), 150 and 240 minutes after the start of circulation. LPS measurement was carried out by mixing the prepared serum sample with LAL reagent at 1:1 ratio in a measuring tube.
Results. All columns can reduce endotoxin levels below the 12.5 µg and even 50 µg levels, although none of devices were able to reduce the LPS level from “supercritical” 50 µg to “critical” 12.5 µg. However, at the same time, the capacity of the Toraymyxin PMX-20R column turned out to be 5-13 times greater than that of other products. This result suggests that while removing endotoxin under similar conditions, the Toraymyx in PMX-20R column will have a much higher reserve of sorption capacity and, therefore, greater opportunities for lowering a risk of septic shock progression.
Conclusion. The study we presented provides insights into whether sorption capacity of the tested cartridges is sufficient to remove endotoxin at initial (12.5 µg) load that corresponds to the onset of systemic inflammatory response syndrome in a typical patient. Additionally, it elucidates to what extent a cartridge can reduce the endotoxin load in severe septic shock with a total LPS load of up to 50 µg.
What is already known about this subject?
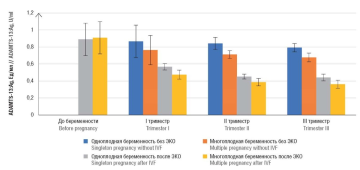
► Elevated level of von Willebrand factor (vWF) is an important thrombosis risk factor. ADAMTS-13 metalloproteinase cleaves ultralarge vWF molecules and lowers its thrombo-
genicity.
► During pregnancy, vWF level increases significantly in the second and third trimesters, ADAMTS-13 antigen (ADAMTS-13:Ag) level decreases starting from the second trimester, staying within the reference range even in the third trimester.
► During in vitro fertilization (IVF), hormonal stimulation increases vWF level and activity accompanied by decreased circulating ADAMTS-13:Ag level.
What are the new findings?
► The chronological sequence of hemostasis gestational adaptation is disrupted by using hormonal ovulation stimulation in IVF programs.
► In twin pregnancy after IVF, vWF level even in the first trimester was 2-fold higher than for non-pregnant women and was significantly higher than the corresponding values in patients with singleton pregnancy after IVF and spontaneous multiple pregnancy.
► A decline in ADAMTS-13:Ag level was observed also from early pregnancy; in bichorial biamniotic pregnancy, the parameter in the first trimester was up to 2-fold lower than that before the onset of ovulation stimulation.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Increase in vWF:Ag, decrease in ADAMTS-13:Ag and disturbance of ADAMTS-13/vWF axis can be used as predictors of gestational adaptation failure and development of gestational and thrombotic complications in multiple pregnancy resulting from applying assisted reproductive technologies (ART).
► Multiple pregnancy after IVF should be considered as a pregnancy with the top risk of gestational adaptation disruption, and discuss an issue of timing for using antithrombotic prophylactic agents.
Aim: to compare changes in the ADAMTS-13 metalloproteinase/von Willebrand factor (vWF) axis in pregnant women with spontaneous or following in vitro fertilization (IVF) singleton and bichorial biamniotic pregnancies.
Materials and Methods. A prospective observational randomized controlled trial was conducted. The examination data of pregnant women with singleton (group 1, n = 34) and multiple bichorial biamniotic spontaneous pregnancies (group 2, n = 17), and with singleton (group 3, n = 34) and multiple bichorial biamniotic pregnancies (group 4, n = 34) following reproductive technologies were analyzed. The studied parameters included quantitation of ADAMTS-13 antigen (ADAMTS-13:Ag), ADAMTS-13 activity (ADAMTS-13:Ac) and vWF antigen (vWF: Ag) by chromogenic enzyme immunoassay.
Results. A progressive increase in the vWF:Ag level has been revealed that was proportional to escalating gestational age and a decrease in ADAMTS-13:Ag level from the second trimester of physiological non-induced pregnancy, more profound during twin pregnancy (p < 0.001). In induced pregnancy, vWF:Ag level increased, ADAMTS-13:Ag - decreased starting from 6-7 weeks of gestation (p < 0.001), more prominent in twin pregnancy (p < 0.001). The ADAMTS-13 activity in induced single and multiple pregnancies did not differ significantly by trimester but was lower compared with non-induced pregnancies of matched timeframe. The most pronounced decrease in the ADAMTS-13:Ag/vWF:Ag ratio was observed in multiple induced pregnancies.
Conclusion. Stimulation of superovulation and subsequent embryo transfer into the uterine cavity is accompanied by higher procoagulant vascular endothelium properties, vWF release, which activates platelets and the coagulation cascade from the early stages of induced pregnancy. vWF hyperreactivity is compensated by the expenditure of ADAMTS-13, which level declines dramatically during twin pregnancy creating conditions for disruption of hemostasis gestational adaptation and increases a risk of thrombotic complications and obstetric pathology.
REVIEW ARTICLES
What is already known about this subject?
► Endometriosis possesses a multifactorial genetic potential and various epigenetic abnormalities may play an important role in its pathogenesis.
► Chromatin modifiers affect gene expression by regulating methylation processes and altering DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) activity, which leads to affected epigenome activity.
► Changes in epigenome activity can contribute to development of endometriosis by disrupting the regulation of genes associated with proliferation, apoptosis and angiogenesis.
What are the new findings?
► DNA hypermethylation of local cells due to increased expression of DNMT1, DNMT3A and DNMT3B is observed in endometriosis.
► Decreased expression of genes such as human homeobox A10 (HOXA10), which regulates the growth, differentiation and implantation of the endometrial embryo is associated with a decrease in uterine susceptibility and the occurrence of endometriosis-related infertility.
► In endometriosis, the microRNA spectrum changes, which additionally affects the expression of the corresponding target mRNAs. For example, microRNA-135a/b, which regulates HOXA10, is activated in endometriosis and causes progesterone resistance. MicroRNA-199 is suppressed, therefore cyclooxygenase-2 translation is not suppressed, which leads to arising pro-inflammatory environment, characterized by active prostaglandin synthesis and an increased interleukin-8 concentration.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Changes in histone acetylation and methylation patterns can contribute to abnormal proliferation and invasion of endometrial cells implying that the development of drugs capable of regulating such events may become a new direction in treatment of endometriosis.
► Understanding the role of chromatin modifiers may lead to creation of more precise diagnostic tests able to detect early-stage endometriosis. This, in turn, will allow to apply treatment earlier and prevent development of complications.
► Drugs that regulate histone acetylation and methylation can be used to prevent developing endometriosis in women at risk.
Introduction. It was revealed that various epigenetic abnormalities may play an important role in the endometriosis pathogenesis. The regulation of chromatin structure is carried out mainly by chromatin modifiers (CMs), which stimulate generation of genomic regions with different functional structures and thus change the patterns or levels of gene expression by exerting expected biological functions and causing epigenetic changes.
Aim: to consider CMs role in endometriosis pathogenesis and their regulation mechanism assessing current publications.
Materials and Methods. The search was conducted in the databases PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, Google Scholar and eLibrary. Keywords and phrases in Russian and English related to the research topic were used as follows: "endometriosis", "chromatin modifiers", "histone acetylation", "DNA methylation", "microRNA". The evaluation of articles was carried out in accordance with PRISMA recommendations.
Results. Chromatin modifiers control differentiation, growth and development, aging and cell death by interacting with various functional chromatin elements. They can cause abnormal gene expression by regulating chromatin structure affecting emergence and development of endometriosis. DNA methylation determines cell types, controls gene expression and genome stability. Abnormal DNA methylation in gene promoter regions necessary for normal endometrial response affects endometriosis development. DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) inhibitors reduce the methylation of human homeobox A10 (HOXA10) and progesterone receptor (PR) genes and potentiate their expression in endometrial cells, improving endometrial susceptibility and inhibiting cell cycle progression. Abnormal histone modifications in endometrial cells may facilitate or hinder the access of transcription mechanisms to chromatin DNA. Histone deacetylase inhibitors effectively eliminate the effects of abnormal histone modifications in endometriosis cells and prevent endometriosis progression. The expression of non-coding RNAs and chromatin remodeling complexes also alters chromatin structure being involved in arising endometriosis and is associated with infertility by promoting proliferation, invasion and migration of endometrioid cells.
Conclusion. Chromatin modifiers play a key role in developing endometriosis by controlling gene expression and chromatin structure. Understanding underlying mechanisms provides valuable information for diagnostics and development of new approaches to treat endometriosis.
What is already known about this subject?
► Placentation abnormalities include pathological invasion of the myometrium, as well as altered placenta and umbilical cord location, morphology.
► The major factors of abnormal placentation are considered to be related to invasive intrauterine interventions, uterine scarring, chronic endometritis and uterine malformations.
► Placental abnormalities are associated with higher rate of cesarean sections, maternal and perinatal morbidity and mortality.
What are the new findings?
► It has been increasingly evident that abnormalities of placental attachment and use of assisted reproductive technologies (ART) have a clear relation.
► Ultrastructural differences with regard to the morphology of placental hematopoietic barrier were demonstrated in mothers whose pregnancy occurred due to in vitro fertilization, compared with spontaneous pregnancy.
► When transferring thawed embryos, a higher rate of premature detachment of the normally located placenta was observed, whereas the rate of placenta previa, on the contrary, was higher in the "fresh" cycle.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► It is possible to develop a modified risk scale for obstetric bleeding, in accordance with the data obtained on the high risk of placental abnormalities in post-ART women.
► Due to the increased risk of placental abnormalities, and, consequently, maternal and perinatal morbidity and mortality, post-ART patients should be closely monitored in antenatal clinic and maternity hospital.
► The increased rate of placenta accretion after using ART confirms the need for ultrasound screening of such patients by specialists experienced in visualizing such pathology.
Placentation abnormalities resulting from using assisted reproductive technologies (ART) is a pressing global obstetrical issue due to complications associated with the pathology: bleeding during pregnancy, postpartum hemorrhage, higher number of cesarean sections, perinatal and maternal morbidity and mortality. This pathology rate tends to increase also due to higher number of pregnancies achieved via in vitro fertilization (IVF). In this regard, we decided to find out the key risk factors for developing this pathology, identify new international data on placentation abnormalities, ART impact on this disease, since ART have been increasingly used to achieve pregnancy in women, both in Russia and abroad. Recent studies have proven the unique morphological structure of the placental hematopoietic barrier in post-IVF women as well as an increased incidence of placentation abnormalities, placenta accreta and premature abruption in comparison with spontaneous pregnancy.
What is already known about this subject?
► The immune system plays an important role in female reproductive function, from implantation to pregnancy maintenance. Changes in the immune system play a key role in the etiology and treatment of various infertility forms, including general infertility, idiopathic infertility (II), recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL) and recurrent implantation failure (RIF).
► Reproductive immunological disorders are considered to be quite common among patients with II, RPL, and RIF. However, reproductive immunology is not a fully established and recognized discipline.
What are the new findings?
► Immunological tests can play an important role in infertility diagnostics and treatment. However, only testing for antiphospholipid antibodies (APA), thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and anti-thyroperoxidase antibodies (TPOAb) has proven effectiveness.
► APA are significantly associated with poor-quality embryos, metaphase II eggs, blastocysts, as well as with lowered rate of implantation, clinical pregnancy and live birth. The presence of APA negatively affects assisted reproductive technologies (ART) results. Thus, it is necessary to carry out immunological testing for APA while choosing infertility therapy methods.
► A high level of anti-TPOAb antibodies negatively affects the outcome of pregnancy during ART, even in patients with euthyroidism.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Immunological testing can potentially be an effective tool in determining the cause of infertility and miscarriage by detecting immune system disorders. This allows to prescribe more targeted and effective treatment.
► Based on the results of immunological tests, it is possible to develop individual treatment plans, which will increase the odds of successful conception and gestation.
► Detection and correction of immune disorders before pregnancy will reduce a risk of miscarriage and other complications associated with immune system disorders.
Introduction. According to various estimates, in Russia 10 to 20 % of people of reproductive age are infertile. Changes in the immune system play a key role in the etiology and treatment of various infertility forms. The active introduction of immunological testing into clinical practice can potentially improve the results of infertility diagnostics and treatment.
Aim: to analyze the current literature data on immunological testing in female infertility, as well as to assess its potential role in infertility diagnostics and treatment.
Materials and Methods. There was conducted a search for publications in the electronic databases PubMed and eLibrary by using the following keywords and their combinations: "infertility", "immunology", "immune system", "immunological testing", "diagnostics", "treatment". The articles were evaluated in accordance with the PRISMA recommendations. Ultimately, 88 publications were included in the review.
Results. Testing for antiphospholipid antibodies (APA) may be useful for women undergoing assisted reproductive technology (ART) therapy, as these antibodies increase the risk of pregnancy complications and thrombotic risks associated with ovarian stimulation, but studies assessing AFA effect on in vitro fertilization (IVF) outcomes have ambiguous results. The presence of antithyroid antibodies (ATA) may be associated with infertility, so their assessment is indeed important to determine treatment tactics. It has been suggested that antinuclear antibodies (ANA) may affect reproductive function by disrupting trophoblast cell development and interfering with RNA transcription, which may lead to lowered reproductive success. Studies have shown that patients with a positive ANA data have a lower incidence of pregnancy and a higher rate of miscarriages after IVF procedure. The human herpes virus type 6 (HHV-6) affects female fertility and is often the cause of spontaneous termination of pregnancy. B-cell lymphoma protein 6 (BCL-6) can serve as an important prognostic biomarker to identify individuals with endometriosis and related reproductive disorders, including idiopathic infertility. Evaluation of endometrial decidualization can be a useful tool to assess readiness for endometrial implantation and provide opportunities for targeted therapeutic interventions. The issue of testing for NK-cells in patients undergoing infertility screening remains controversial due to the difficulties of standardizing testing recommendations.
Conclusion. To date, there is a limited number of reliable data on the role of various immunological tests in infertility diagnostics and treatment. With the exception of testing for AFA in patients with RPL, as well as for thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and anti-thyroperoxidase antibodies (TPOAb) in patients undergoing therapy using various types of assisted reproductive technologies, the remaining immunological tests provide scant data to justify their routine use in clinical practice. The major limitations of existing studies are coupled to a small patient sample, as well as heterogeneity of inclusion criteria, patient groups and research methods.
What is already known about this subject?
► Artificial intelligence (AI) has been extensively developing in various medical specialties, especially those related to data visualization.
► AI has the potential to overcome the limitations of manually evaluated medical images while improving diagnostic accuracy.
► AI has a great and recognized potential to assist in repetitive tasks such as automatic identification of good-quality images and identification of visualization patterns.
What are the new findings?
► AI-based models allow to effectively diagnose and predict course of cervical cancer.
► Several AI models (clinical, biochemical, and radiological) have been developed for the early, minimally invasive diagnostics of endometriosis. The main purpose of such algorithms is to decrease number of diagnostic laparoscopies.
► AI demonstrated high diagnostic and prognostic efficacy in endometrial cancer and ovarian cancer, which can markedly lower related mortality.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► In the field of oncogynecology AI provides an opportunity to establish an earlier diagnosis able to result in decreased mortality.
► AI is an extremely profitable solution for modern gynecology because it saves time and resources.
► AI cannot fully replace doctors, but it may perfectly integrate into clinical practice, assisting in decision-making process and reducing errors in differential diagnostics and variability in interaction between different medical specialists.
Introduction. Artificial intelligence (AI) is a technology that simulates human brain data processing, its intellectual behavior and critical thinking. Sophisticated AI models can potentially improve patient management by speeding up processes and increasing their accuracy and efficiency at a lower cost of human resources. Compared to other specialties, use of AI in gynecology remains in its infancy. It is important to understand that the available methods for clinical imaging have certain limitations, namely clinician's workload and data variably interpreted by different doctors. AI, in turn, has the potential to overcome these limitations while increasing diagnostic accuracy.
Aim: to structure and analyze current published data on AI use in gynecology.
Materials and Methods. A search for primary sources was carried out in the electronic databases PubMed, eLibrary and Google Scholar. The search queries included the following keywords "artificial intelligence", "gynecology", "endometrial cancer", "endometriosis", "ovarian cancer", "diagnostics", "oncogynecology" retrieved from February 2014 to February 2024. Articles were assessed according to PRISMA guidelines. After identification, before the screening stage, duplicates were excluded. At the screening stage, the titles and annotations of the identified articles were analyzed for eligibility to the review topic as well as for available full-text versions; abstracts and letters to the editorial board in scientific journals were excluded at this stage. 685 full-text articles were evaluated for eligibility, the inclusion criteria were as follows: publication in Russian or English; the study describes use of AI technologies in diagnostics or treatment of gynecological diseases. All disagreements between authors were resolved by consensus. Ultimately, 80 primary sources were included in this review.
Results. AI-based systems have succeeded in image analyzing and interpreting and over the past decade have become powerful tools that have revolutionized the field of gynecological imaging. In the studies analyzed, AI was able to provide faster and more accurate forecasts and diagnostics, increasing the overall effectiveness of gynecological care. It is important to note that AI cannot fully replace doctors, but it can perfectly integrate into clinical practice, helping in the decision-making process and reducing errors in differential diagnosis and variability of interaction between different specialists. In the field of oncogynecology, undoubtedly one of the most promising aspects is the possibility of better and especially early diagnostics and, ultimately, improved patient survival.
Conclusion. A great success has been achieved so far, and AI use is expected to extend in the next few years. In fact, it will take a very long way to go before AI-based technologies are fully integrated into clinical practice.
CLINICAL CASE
What is already known about this subject?
► Every third newborn with meconium aspiration syndrome (MAS) requires tracheal intubation and start of mechanical ventilation, with mortality rate reaching as high as 20 %.
► In order to avoid the use of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), surfactant replacement therapy is often used worldwide: surfactant lung lavage or bolus injection. Surfactant therapy of neonatal acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) in MAS reduces mortality and disability.
► Most researchers use a surfactant solution for lavage in a volume of 15–20 ml/kg, and cases of repeated bolus surfactant administration after lavage have also been described. No similar studies on this topic were found among studies published in Russian.
What are the new findings?
► This review and the case report provide an insight about safe and effective use of the respiratory strategy of surfactant lung lavage in the amount of 15–20 ml/kg and/or bolus surfactant administration in severe MAS.
► A successful experience of using surfactant lung lavage with subsequent bolus surfactant injection in a newborn complicated with air leak syndrome (ALS), persistent pulmonary hypertension of newborns and neonatal ARDS in MAS is presented.
► For the first time in Russia, the algorithm of surfactant lung lavage with bolus surfactant administration has been described to improve oxygenation and prevent ECMO.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Our experience provides additional opportunities for surfactant therapy in neonatal clinics in the case of severe MAS, when the start of ECMO and/or transportation to the ECMO center is not possible due to the severity of patient's condition.
► Such respiratory strategy in neonatology can reduce a risk of ECMO and lead to improved oxygenation as well as rapid stabilization of patients with MAS, lower ALS risk.
► Our study may represent a successful application of this respiratory strategy in newborns with severe MAS.
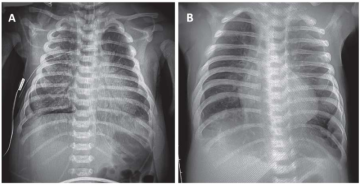
Here, we review the latest available studies on using surfactant lavage in newborns with severe manifestations of meconium aspiration syndrome (MAS), illustrated by a representative clinical case. Meconium-stained amniotic fluid may be found in 8-20 % of all births, with the incidence reaching 23-52 % after a full 42 weeks of gestation. From 2 to 9 % of newborns with meconium-stained amniotic fluid subsequently develop MAS clinical signs. About a third of newborns with MAS require tracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation. MAS-related mortality rate due to severe injuries of the lung parenchyma and the development of pulmonary hypertension, can exceed 20 %. Other complications, including air leak syndrome (ALS), occur in 10-30 % of children with MAS. Surfactant lavage may be one of the clinical tools that avoids extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) in severe MAS cases. This clinical observation is also of interest because a mature, even post-term newborn with MAS subsequently developed a typical bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD), which required proper treatment.
FROM HISTORY
The article is devoted to the 150th birth anniversary of the famous Russian and Soviet obstetrician-gynecologist Vasily Vasiliyevich Preobrazhensky (1874-1944), became in 1934 the first head of the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology at the Arkhangelsk State Medical Institute, who laid the foundation for development of the Northern Scientific School of Obstetrics and Gynecology.
In this article we review the history of the thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA) study over the past 100 years. Important events and discoveries made by scientists across the globe are described, which profoundly contributed to understanding TMA etiology, pathogenesis and treatment. The prospects for current TMA investigation especially in obstetric practice are discussed.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
ISSN 2500-3194 (Online)